Stationary power generation is at the heart of modern energy infrastructure. Understanding stationary power generation is more important than ever for energy tech leaders. Amid the rising electricity demand and changing energy needs, stationary power generation is the need of the hour. It powers urban development and industrial expansion. Technological advancements and policy shifts toward decarbonization emphasize the need for stationary power generation, making it a critical asset for shaping the energy systems of tomorrow. This article will explore the concept of stationary power generation in its entirety.
What Is Stationary Power Generation?
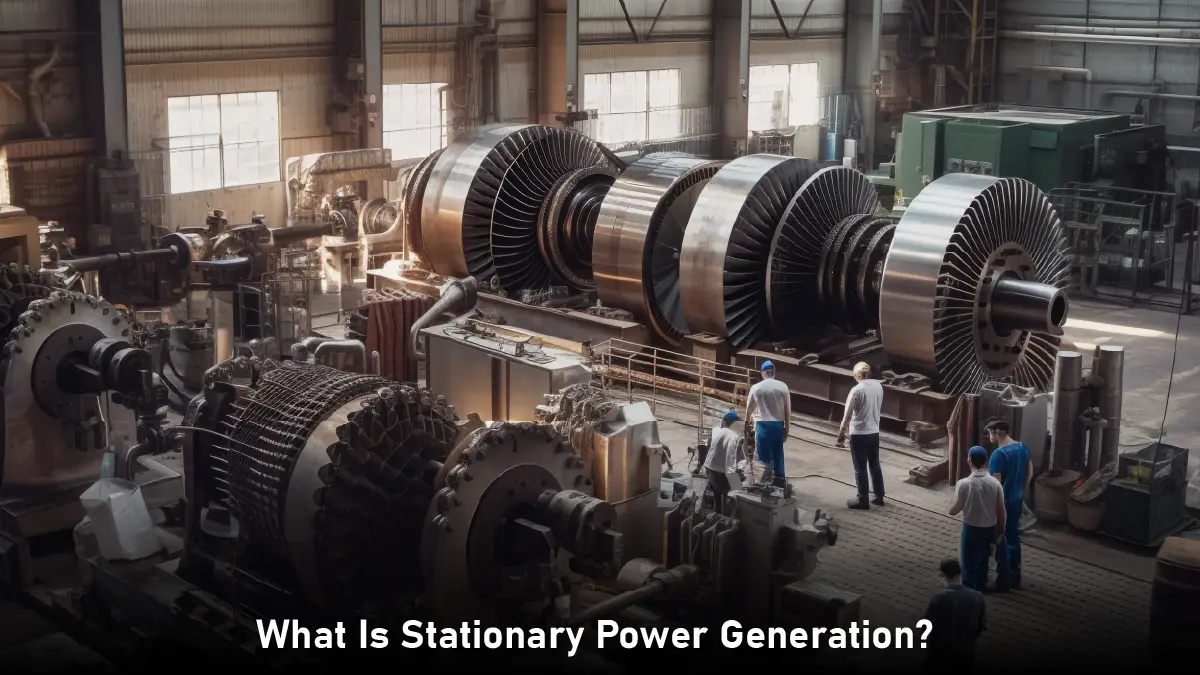
Stationary power generation refers to electricity production at a fixed location. It ensures reliable power supply to residential, commercial, industrial, and critical infrastructure. Unlike portable generators, they are installed and designed for continuous or emergency power supply. They range from small generators for individual buildings to large power plants for entire cities. Stationary power generation also provides backup power during outages. As a primary or secondary power source, stationary power generation is the backbone of modern life and economy.
Core Technologies in Stationary Power Generation
Stationary power generation involves the use of several technologies that help it make a dependable power source. One of them is Conventional Generators that run on diesel, natural gas, or propane. They are backup power sources for data centers, hospitals, and industrial facilities. They are reliable, start up fast, and scalable to meet large power demands.
Stationary Fuel Cells became popular as a clean and efficient power source. Fuel cells (PEMFCs, SOFCs, DMFCs) generate electricity through electrochemical reactions. This means low emissions, quiet operation, and minimal maintenance. Such fuel cells are used to provide primary and backup power for tech companies, telecom networks, retail outlets and other critical infrastructure sectors.
Renewable Energy Systems are adopted in stationary power generation as part of sustainability. Solar Photovoltaic (PV) technology has distributed and utility-scale applications. Wind power is often irregular and unreliable. Integrations with battery storage or backup generators helps overcome its intermittent nature. Battery storage systems support peak electricity demands and prevent fluctuations in renewable energy supply.
Also Read: Why Remote Care Management Is Becoming a Core Component of Value-based Care
Emergence of Hybrid and Microgrid Solutions is changing the concept of stationary power management. Hybrid systems integrate conventional generators, renewable sources, and battery storage systems for power generation. This promotes high output and efficiency. Microgrids in hospitals and university campuses help them to operate during power outages. This powerful alternative ensures uninterrupted power supply. These core technologies form the foundation of modern stationary power generation.
Recent Developments in Stationary Power Generation
- Stationary fuel cells to reach USD 7,011.1 million by 2031 as decentralized power generation and reliable energy supply gain importance.
- Big investments in hydrogen production and storage for next-gen fuel cell systems.
- AI-powered energy management and smart monitoring for predictive maintenance and high power efficiency.
- 63 GW of new utility-scale electricity generating capacity to be added by the U.S. in 2025 with 81% of being solar and battery storage.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) for carbon-free and reliable power, with more adoption in data centers and industrial applications.
Applications of Stationary Power Generation
| Sector | Applications | Key Benefits |
| Residential | Home backup, off-grid cabins | Uninterrupted power supply, energy savings |
| Commercial | Retail stores, office buildings, telecom towers, data centers | Reliability, grid support, sustainability |
| Industrial | Factories, refineries,
chemical plants |
Steady production, improved safety |
| Critical Infrastructure | Hospitals, emergency services, military bases | Continuous power,
guarantees uptime |
| Utilities | Power plants,
distributed generation, renewable energy projects |
Grid stability,
manages peak demand, aids decarbonization efforts |
Case Studies
Several case studies show the importance of stationary power generation in ensuring energy supply across various sectors. A data center in Silicon Valley had frequent power outages so they installed multiple 2.5 MW diesel generators with by a 10 MVA lithium-ion UPS and smart control systems. This setup kept 100% uptime during major grid disruptions. It proved the need for stationary power systems for mission-critical IT infrastructure.
Similarly, a large hospital in NYC installed a microgrid with diesel and natural gas generators, UPS for critical departments, solar panels, and battery storage. This integrated system delivered medical services during blackouts, improved patient safety, and reduced dependence on external fuel supplies.
Stationary power generation is also essential in landfill gas-to-energy projects. A combined cycle system in Orange County, California, captures landfill gas to generate 32.5 MW. It saves a whopping 32,000 gallons of water daily. Meanwhile, a smaller-scale project in Watauga County, North Carolina, uses modified automotive engines to produce 186 kW and makes US$ 72,000 in annual profits. It serves as a model for community-scale power generation.
In Houston, Texas, an industrial petrochemical plant deployed 3 MW diesel generators with large-scale battery storage and a centralized control system. This solution kept the plant running during outages, improved safety, and minimized production losses.
Future of Stationary Power Generation

Stationary power generation appears to have a very bright future. Renewable energy like solar and wind is growing fast because of dropping costs and supportive governments. Batteries and other energy storage systems help keep the power steady in the absence of renewables. Fuel cells are gaining attention as a clean way to generate power, and SMRs offer a new, safe, and carbon-free form of energy that many companies and industries are interested in.
Decarbonization is a big reason why stationary power is growing. It helps bring more clean energy like renewables and hydrogen into the system. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) like and solar-plus-battery setups are changing how the grid works and giving consumers more control over their energy. Government incentives, green energy rules, and net-zero goals are pushing the expansion of stationary power solutions globally.
Stationary power generation will be more diverse, efficient, and green in the future. It will meet the world’s growing energy needs while helping us move toward a cleaner, low-carbon future.
In Conclusion
Stationary power is a steady and reliable way to provide energy to homes, businesses, factories, and important services. As we need more energy and want cleaner options, these systems are becoming more important. Whether it’s traditional generators, fuel cells, solar batteries, or new technology like SMRs, stationary power helps keep the lights on. Energy leaders need to learn about and use these technologies to build a stronger, cleaner, and more reliable energy future for everyone.
Remember, Energy Tech Leaders!
Stationary power keeps the electricity grid stable, supports important services, and helps the world use cleaner energy.
New technology, helpful laws, and growing demand are making stationary power popular and shaping its future.




